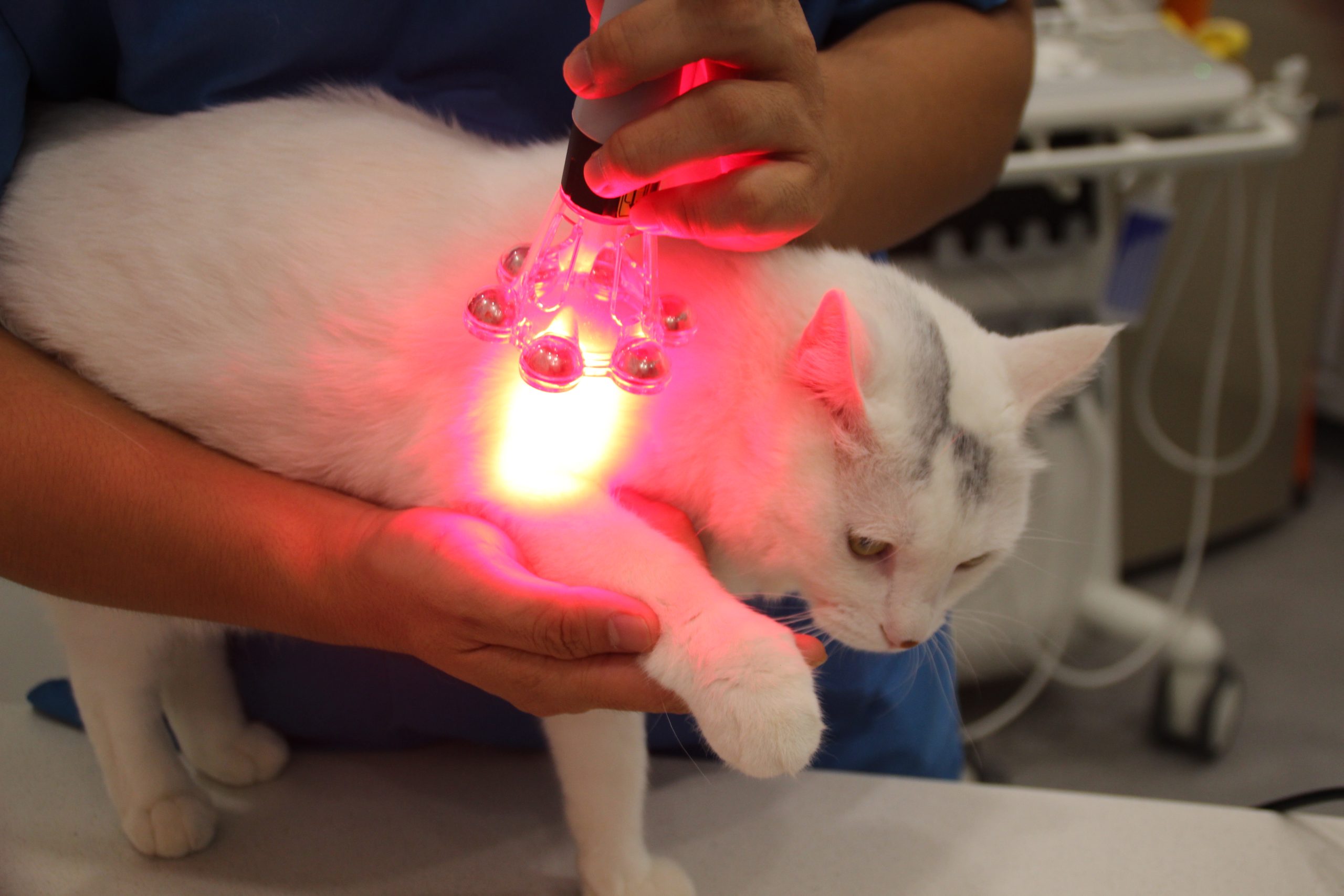
Laser Therapy: A Modern Solution for Pet Sports Injuries
Pets are essential companions in our lives, but they are also susceptible to various sports injuries during physical activities. Laser therapy devices offer a modern approach to addressing these injuries in veterinary medicine. This article delves into the principles and distinctions of laser veterinary medicine in treating pet sports injuries, highlighting its advanced nature and advantages. Clinical cases are also provided to demonstrate its effectiveness.
Principles and Differences between Laser Veterinary Medicine and Traditional Treatment:
Laser Veterinary Medicine Principles:
Laser veterinary medicine employs laser beams directed at the injured area of the pet's body. These laser beams penetrate the skin and directly affect the damaged tissue. The biological stimulation effect of light promotes cell repair and healing. This treatment aids in:
- Pain Reduction: Laser therapy alleviates pain caused by pet sports injuries, enhancing their overall quality of life.
- Inflammation Reduction: Laser treatment helps reduce inflammation, swiftly eliminating swelling and promoting the repair of damaged tissues.
- Healing Promotion: Laser therapy stimulates blood circulation, increasing the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the injured area, facilitating tissue healing.
- Non-Invasive: Laser therapy is non-invasive, eliminating the need for surgery and reducing the associated risks and recovery time.
Traditional Treatment Methods:
Traditional treatment methods typically include medication, surgery, and physical therapy. These approaches may require an extended duration, exhibit inconsistent results, and involve some degree of invasiveness. Medication treatments may lead to uncomfortable side effects, while surgery necessitates an extended recovery period.
Advantages of Laser Therapy:
- Rapid Pain Relief: Laser therapy often significantly reduces pain in pets after just a few treatment sessions, enabling faster recovery.
- Biological Stimulation Effect: Laser treatment enhances blood supply to damaged tissues, expediting healing and cell repair.
- Non-Invasive Treatment: Laser therapy is non-invasive, eliminating the need for surgery and reducing treatment-related risks.
Clinical Cases:
Case One: A dog with Achilles tendon injury experienced significant pain relief and regained normal mobility after several laser therapy sessions.
Case Two: A injured cat underwent laser therapy, resulting in rapid muscle injury repair and a swift reduction in pain symptoms, eliminating the need for medication dependence.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, laser therapy offers significant advantages in addressing pet sports injuries. Its ability to quickly relieve pain, stimulate biological responses, and provide non-invasive treatment makes it an advanced and effective choice. Supported by clinical cases, laser therapy provides pets with a faster and safer path to recovery.

 Afrikaans
Afrikaans Albanian
Albanian Amharic
Amharic Arabic
Arabic Armenian
Armenian Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani Basque
Basque Belarusian
Belarusian Bengali
Bengali Bosnian
Bosnian Bulgarian
Bulgarian Catalan
Catalan Cebuano
Cebuano Chichewa
Chichewa Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional) Corsican
Corsican Croatian
Croatian Czech
Czech Danish
Danish Dutch
Dutch Esperanto
Esperanto Estonian
Estonian Filipino
Filipino Finnish
Finnish French
French Frisian
Frisian Galician
Galician Georgian
Georgian German
German Greek
Greek Gujarati
Gujarati Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole Hausa
Hausa Hawaiian
Hawaiian Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Hmong
Hmong Hungarian
Hungarian Icelandic
Icelandic Igbo
Igbo Indonesian
Indonesian Irish
Irish Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Javanese
Javanese Kannada
Kannada Kazakh
Kazakh Khmer
Khmer Korean
Korean Kurdish (Kurmanji)
Kurdish (Kurmanji) Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz Lao
Lao Latin
Latin Latvian
Latvian Lithuanian
Lithuanian Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish Macedonian
Macedonian Malagasy
Malagasy Malay
Malay Malayalam
Malayalam Maltese
Maltese Maori
Maori Marathi
Marathi Mongolian
Mongolian Myanmar (Burmese)
Myanmar (Burmese) Nepali
Nepali Norwegian
Norwegian Pashto
Pashto Persian
Persian Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Punjabi
Punjabi Romanian
Romanian Russian
Russian Samoan
Samoan Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic Serbian
Serbian Sesotho
Sesotho Shona
Shona Sindhi
Sindhi Sinhala
Sinhala Slovak
Slovak Slovenian
Slovenian Somali
Somali Spanish
Spanish Sundanese
Sundanese Swahili
Swahili Swedish
Swedish Tajik
Tajik Tamil
Tamil Telugu
Telugu Thai
Thai Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Urdu
Urdu Uzbek
Uzbek Vietnamese
Vietnamese Welsh
Welsh Xhosa
Xhosa Yiddish
Yiddish Yoruba
Yoruba Zulu
Zulu