The Principle Of PLDD
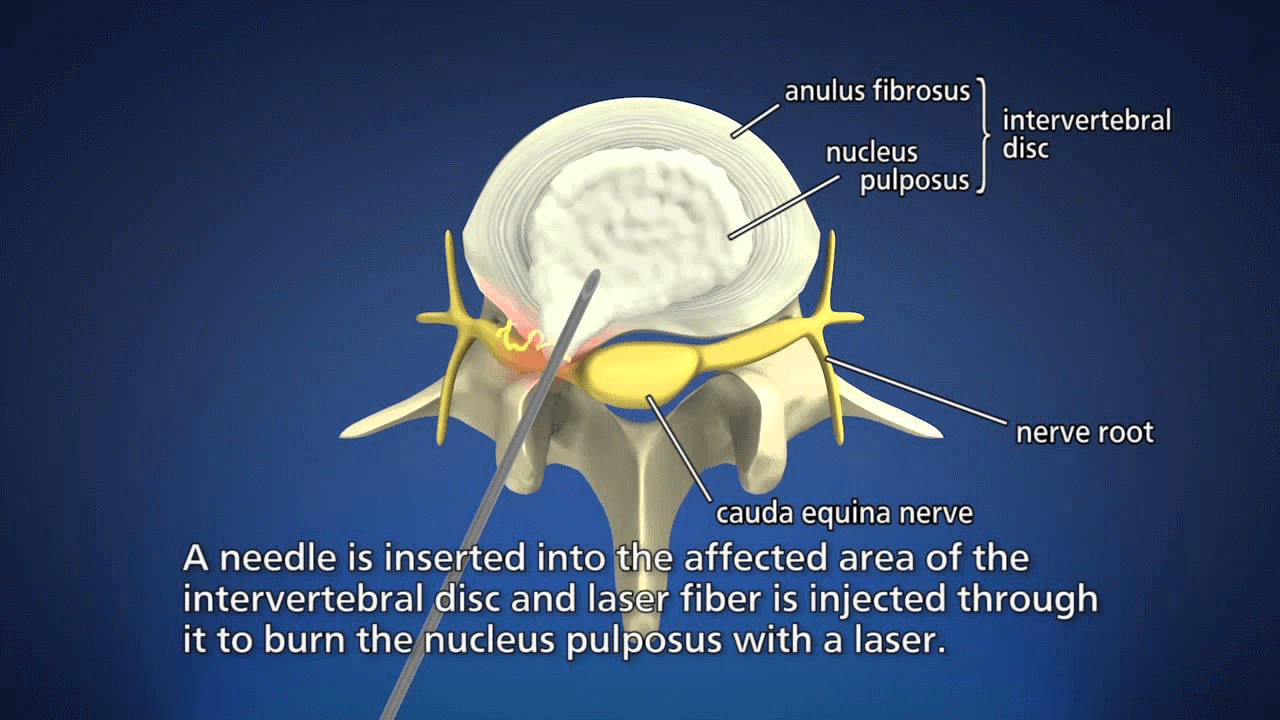
In the procedure of percutaneous laser disc decompression, laser energy is transmitted through a thin optical fiber into the disc.
The aim of PLDD is to vaporize a small portion of the inner core. The ablation of a relatively small volume of the inner core results in an important reduction of intra-discal pressure, thus inducing reduction of disc herniation.
PLDD is the minimally-invasive medical procedure developed by Dr. Daniel S.J. Choy in 1986 that uses a laser beam to treat back and neck pain caused by a herniated disc.
Percutaneous laser disc decompression (PLDD) is the utmost minimally invasive percutaneous laser techniquein the treatment of the disc hernias, cervical hernias, dorsal hernias(except for the segment T1-T5), and lumbar hernias. The procedureuses the laser energy to absorb the water within the herniated nucleuspulposus creating a decompression.
The PLDD treatment is performed on an outpatient basis using only local anesthesia. During the procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the herniated disc under x-ray or CT guidance. An optical fiber is inserted through the needle and laser energy is sent through the fiber, vaporizing a tiny portion of the disc nucleus. This creates a partial vacuum which draws the herniation away from the nerve root, thereby relieving the pain. The effect usually is immediate.
The advantages of laser treatment of PLDD
- It's minimally invasive, hospitalization is unnecessary, patients get off the table with just a small adhesive bandage and return home for 24 hours of bed rest. Then patients begin progressive ambulation, walking up to a mile. Most return to work in four to five days.
- Highly effective if correctly prescribed
- Processed under local, not general anesthesia
- Safe and fast surgical technique, No cutting, No scarring, Since only a tiny amount of disc is vaporized, there is no subsequent spinal instability. Different from open lumbar disc surgery, there is no damage to the back muscle, no bone removal or large skin incision.
- It's applicable to patients who are at higher risk to open discectomy such as those with diabetes, heart disease, decreased liver and kidney functions etc.
Our Related Products
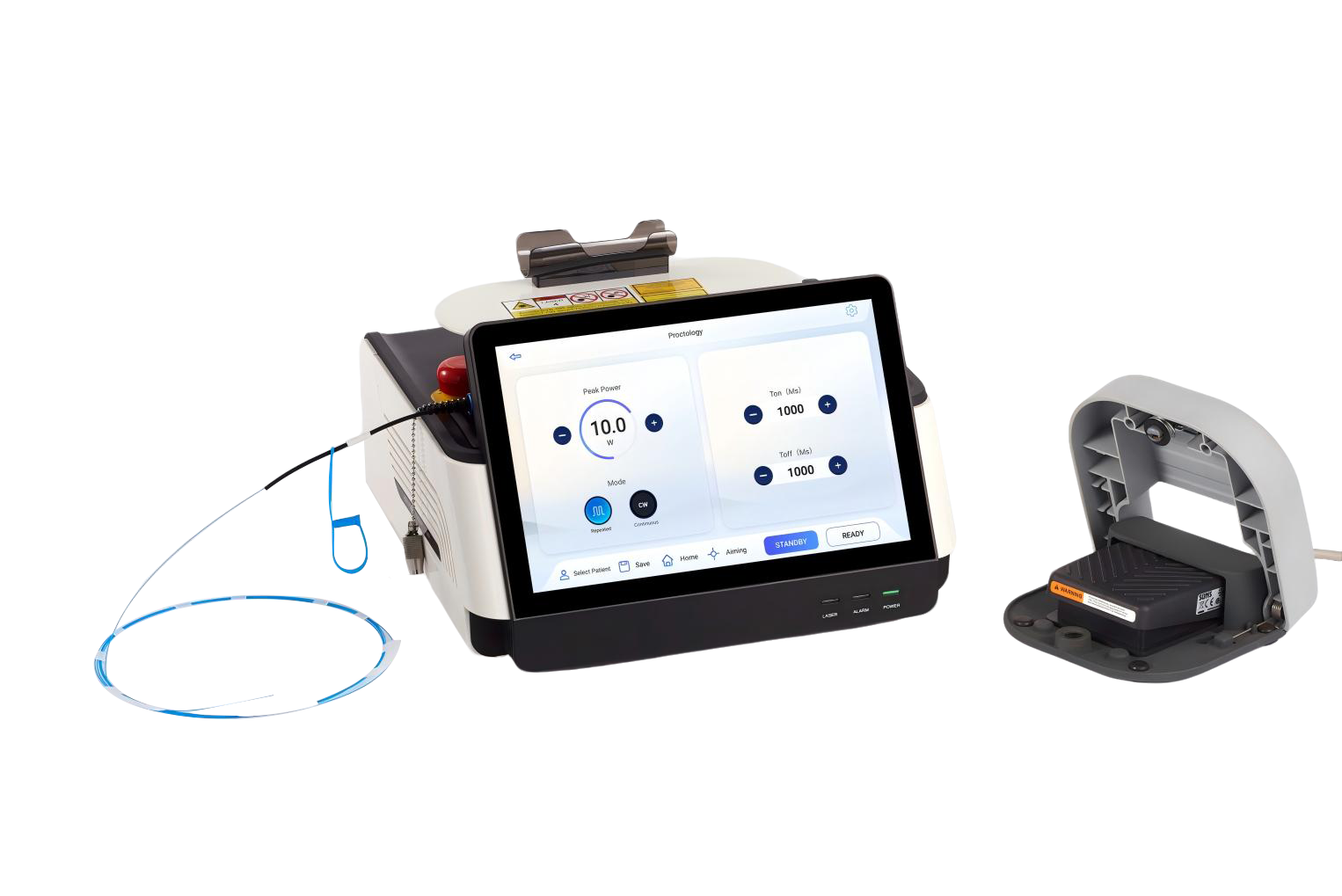

CureLight Series
Percutaneous laser disc decompression (PLDD)